The decentralized finance (DeFi) revolution has transformed how we think about trading and liquidity provision. At the heart of this transformation lies a groundbreaking innovation: Automated Market Makers (AMMs). Unlike traditional exchanges that rely on order books and centralized intermediaries, AMMs use mathematical formulas and smart contracts to facilitate trades automatically. Understanding how these systems work under the hood reveals the elegant simplicity that powers billions of dollars in daily trading volume across decentralized exchanges.
The Core Mechanism: Liquidity Pools and Mathematical Formulas
Traditional exchanges match buyers with sellers through order books—a system that requires sufficient trading activity to function efficiently. AMMs take a radically different approach by replacing order books with liquidity pools. These pools are smart contracts containing reserves of two or more tokens, and trades happen directly against these reserves rather than with other traders.
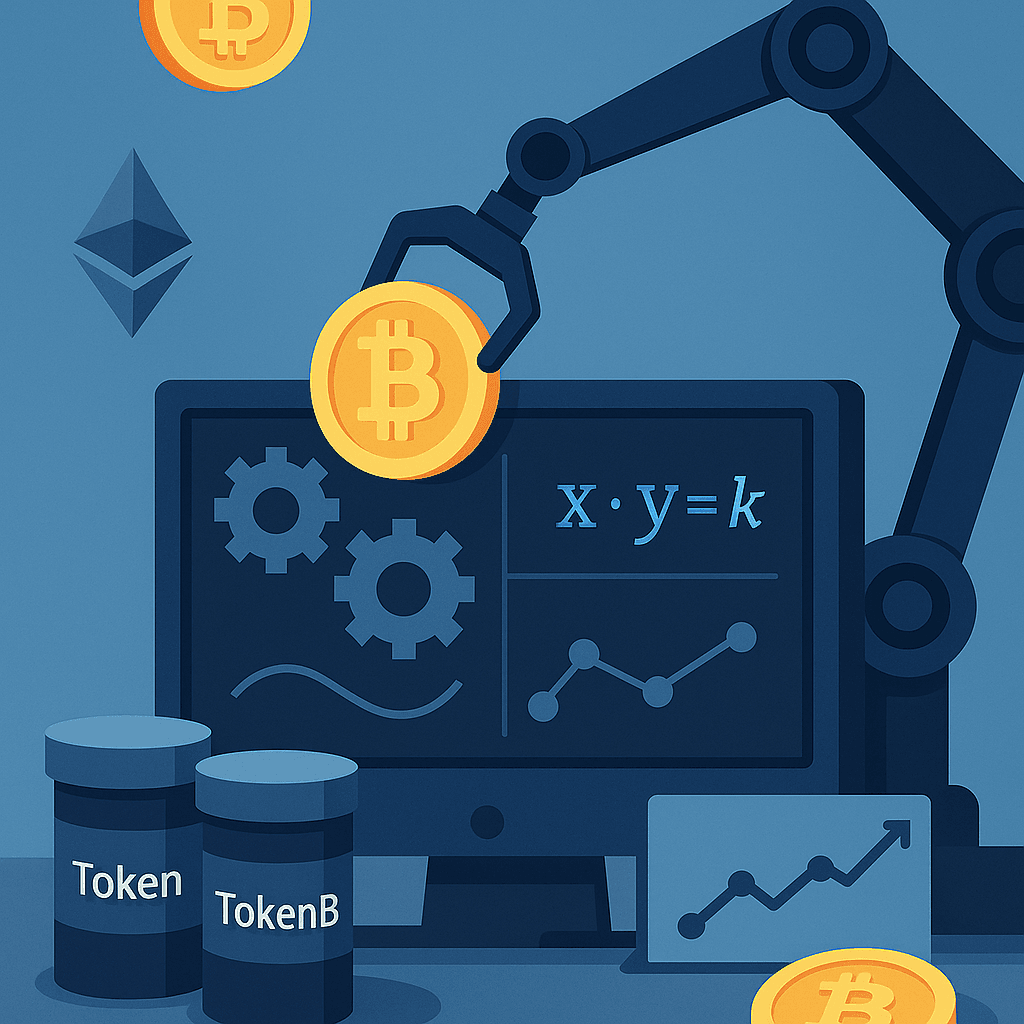
The magic happens through mathematical formulas that determine pricing. The most common formula, pioneered by Uniswap, is the constant product formula: x × y = k. In this equation, x represents the quantity of one token in the pool, y represents the quantity of the other token, and k is a constant that remains unchanged during trades. When someone buys Token A from the pool, they add Token B, decreasing the pool’s Token A supply and increasing its Token B supply. The formula automatically adjusts the price based on this supply change, ensuring the product remains constant.
This mechanism creates what’s known as an automated market maker because prices adjust automatically based on supply and demand—no human market maker required. The larger the trade relative to the pool size, the more significant the price impact, which naturally discourages market manipulation and excessive slippage.
Liquidity Providers: The Backbone of AMM Functionality
AMMs cannot function without liquidity, and this is where liquidity providers (LPs) enter the picture. Anyone can become a liquidity provider by depositing an equal value of both tokens into a liquidity pool. In return, they receive LP tokens representing their share of the pool. These LP tokens can be redeemed at any time to withdraw their portion of the pool, plus any accumulated trading fees.
Liquidity providers earn passive income through trading fees—typically 0.3% per trade on most AMM platforms. Every time someone executes a swap, a small percentage goes to the liquidity providers proportional to their stake. This creates an incentive structure where individuals are rewarded for contributing to the ecosystem’s liquidity depth.
However, liquidity provision isn’t without risks. The primary concern is impermanent loss, which occurs when the price ratio of tokens in a pool changes significantly. If the price diverges substantially from when an LP deposited their tokens, they might end up with less value than if they had simply held the tokens separately. Despite this risk, many liquidity providers find the trading fees and additional incentives offered by DeFi protocols make the strategy profitable over time.
The Evolution and Future of AMM Technology
While the constant product formula remains popular, the AMM space has evolved considerably. Newer models like Curve’s StableSwap formula optimize for stablecoin pairs with minimal price impact, while Balancer allows pools with multiple tokens and customizable weightings. These innovations address specific use cases and improve capital efficiency.
The future of AMMs looks promising with developments in concentrated liquidity, where providers can allocate capital to specific price ranges, and dynamic fee structures that adjust based on market volatility. Layer 2 solutions are also reducing transaction costs, making AMMs more accessible to smaller traders.
Conclusion
Automated Market Makers represent a paradigm shift in how financial markets can operate—removing intermediaries while maintaining efficiency through elegant mathematical principles. By understanding the mechanics of liquidity pools, pricing formulas, and the role of liquidity providers, we can appreciate how AMMs have democratized market making and enabled the explosive growth of decentralized finance. As the technology continues to evolve, AMMs will likely become even more efficient, secure, and integral to the global financial infrastructure. Whether you’re a trader, liquidity provider, or simply a crypto enthusiast, grasping how AMMs work under the hood provides valuable insight into the future of finance.